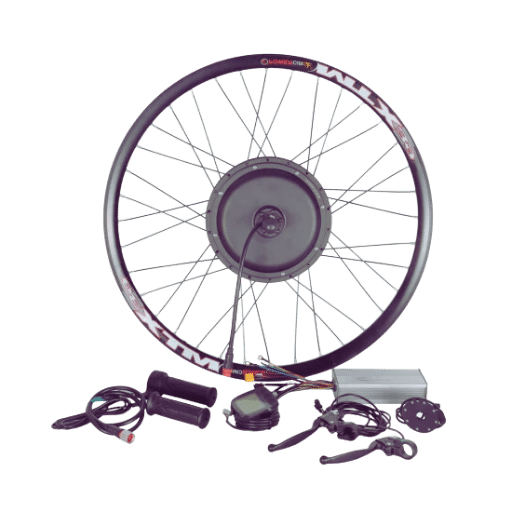
Choosing Between Geared and Direct Drive Hub Motors for Your Electric Bike
Geared Hub Motors
Smaller and lighter in design than direct-drive motors, the most noticeable feature of geared hub motors is this. The motor multiplies torque by means of planetary gears inside it, accelerating faster and performing better on hills. As such, they are well-suited to shuffling around cities or making frequent stops. There could be a little more mechanical sound as well as wearing out over time due to the presence of gear trains, though. While being easy to care for, there may come times when some parts need attention if one wants them running at their best because they have relatively complex inner mechanisms.
Direct Drive Hub Motors
These are sometimes called “gearless” motors because they’re so simple and tough – direct-drive hub motors. They work silently with a few moving components, which also lowers their maintenance requirements. For extended trips where continuous power delivery is necessary, like on cargo bikes, these engines excel at providing steady power throughout long-distance rides. A larger size and weight contribute towards a smoother ride in the case of direct drive motors; however, this can decrease energy efficiency when used at low speeds together with high torque unless accompanied by larger battery capacity compensating for increased power consumption caused by heavier motor weight during such scenarios.
What is a Direct Drive Motor, and How Does it Work?

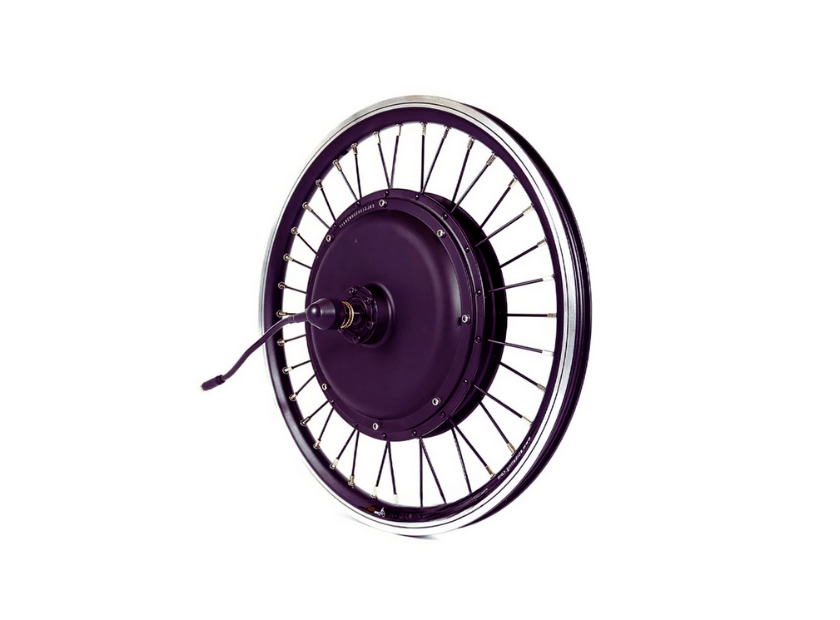
Understanding the Mechanism of Direct Drive Hub Motors
Direct drive hub motors are called “gearless” because they work on a simple principle. They have two main parts: the stator, which is stationary, and the rotor, which moves. When power is supplied to the coils of the stator, a magnetic field is created that makes the rotor rotate. This rotation drives a bicycle wheel directly without any gears or other mechanisms between them. The design is so simple that there are not many things moving, and this means less maintenance with more durability is expected in return for it. Continuous power delivery efficiency is very high due to power being transferred directly from one place to another; therefore, continuous duty applications such as long-distance rides or cargo bikes benefit most from motors like these. Nevertheless, lower-speed energy efficiency can be affected by the size and weight of direct-drive motors; hence, bigger batteries will be required to make up for increased power consumption at low speeds, often resulting from larger batteries used in electric bicycles with heavy direct-drive hub motors.
Advantages of Direct Drive in Electric Bikes
- Low Maintenance: Fewer moving parts are found in direct drive motors compared to geared ones, which means less wearing out. The simplicity of this construction reduces the frequency of fixing or maintaining it.
- High Durability: Absence of gears and strong structure contribute towards making direct drives more long-lasting than any other type of motor. This feature enables the machine to withstand heavy duty applications for long periods without breaking down easily.
- Quiet and Smooth Operation: There are no mechanical noises produced during its operation due to lack of gears used in them. The smoothness and silence exhibited by these motors while running greatly enhance riding experience as a whole.
- Efficient Power Transfer: Energy is transferred from the motor straight into the wheel by direct drive motors thus reducing power wastage through unnecessary conversions. For instance; when one wants to go for a long distance ride continuously like commuting or transporting cargo over sustained period then this kind of effective energy delivery becomes very important.
- Regenerative Braking: Many electric bicycles with direct drive come fitted with regenerative braking systems. This means that when you brake, the motor can work as a generator too thus changing kinetic energy into stored electrical energy which can be used later on thereby increasing battery life more so for those who may want to travel far using these bikes.
- Better High Speed Performance: Direct drive motors perform at their best on higher speeds because they provide constant power without being limited by gear ratios as other types do. Such features make them perfect choice among riders frequenting highways or requiring quicker acceleration rates.
- Heat Generation Reductions: Efficient dissipation is enabled within direct drives by their design. These kinds of motors tend to stay cooler since there are few parts moving against each other, causing friction, hence better performance and longer lifespan due to improved efficiency, especially if used over extended periods where much heat would have been generated otherwise, leading to faster wear-out times thus saving money spent in maintenance costs related with replacing worn-out components caused by excessive heating effects on such machines.
- Increased Torque Output: At high speeds direct drives deliver more pulling power than any other motor because they produce higher torques under such circumstances. Therefore, this makes them appropriate for applications needing considerable amounts of pulling forces like towing heavy loads up steep hills.
- Eco-Friendly Nature: The overall energy consumption is reduced through regenerative braking system and efficient power transfer mechanisms used in direct drive motors. In turn, it leads to lower environmental impacts thereby contributing towards sustainable transport solutions.
- Simple Design: The design simplicity associated with direct drive motors allows for easy integration into various electric bike frames. This means that different kinds of bikes can be made without compromising on performance or efficiency levels as provided by these types of motors.
Direct Drive vs Geared Hub Motors: A Comparison
When you compare direct drive motors to geared hub motors, you must look at several differences in technical parameters.
Efficiency and Power Delivery: At higher speeds, direct-drive motors are generally more efficient because they offer constant power without gear ratio limits. Conversely, lower-speed performance is where geared hub motors shine since they provide better torque for stop-and-go urban riding efficiency.
Maintenance and Durability: Direct-drive motors have fewer parts that move; thus, they tend to wear out less over time. This means lower maintenance needs and longer life spans. However, internal gears in geared hub motor systems may wear down faster than other components – requiring frequent servicing due to gear or bearing damage.
Size and Weight: The size of a direct drive motor is usually larger than the equivalent geared hub motor because of its structure. As a result, this can affect weight distribution on bikes as well as overall design choices available when building them up into complete bicycles using different frame types, etc. On the other hand, geared hub motors are smaller in size compared with their direct-drive counterparts, which makes them lighter, too, thereby making integration into compact, lightweight frames easier.
Torque and Acceleration: Better acceleration from standstill or climbing hills is easily achievable through higher levels of starting torque produced by geared-hub motors, especially during low-speed operation. Direct-drive versions will give smoother power delivery over wide ranges but might suffer slightly at very low-speed regions where more twisting force is needed for take-off.
Noise Levels: Direct drive motors operate quietly since they lack internal gears that can cause an audible whirring sound when rotating against each other while in motion unlike those found within some types of geared-hub motor assemblies where such noise could be produced due to teeth engagement between mating pairs leading to rapid transmission losses accompanied by heat generation during operation under heavy loads etcetera.
Heat Generation and Dissipation: In terms of dissipating generated heat energy related to frictional forces created within these two types of motors, direct drive variants tend to do so better than geared hub counterparts. This is achieved by efficient heat management systems incorporated into the former which enhances their performance efficiency and extends its useful life while reducing wear and tear on components. However, more gear engagements taking place between different stages along transmission pathways inside GHM during operation under high torque conditions may result in increased temperatures requiring additional cooling mechanisms for proper functioning.
Energy Regeneration: Unlike geared-hub configurations, the regenerative braking feature commonly found in most DD motors enables the conversion of kinetic energy back into electrical power, thereby prolonging the battery pack lifespan. Geared hubs rarely have this capability, though there exist few designs that allow some amount of energy recovery during deceleration events like downhill coasting, etcetera.
To sum up, the decision between a direct-drive motor and a geared hub depends on factors such as the required speed range, terrain type, and maintenance considerations. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages based on technical specifications, but both are good options depending on how they will be used operationally.
Exploring Gear Hub Motors for E-Bikes
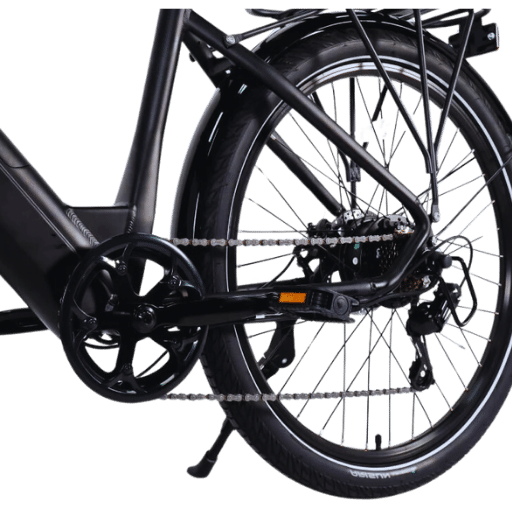

The Basics of Geared Hub Motor Technology
The e-bike’s geared hub motors integrate a range of internal gears which enhance torque output; thus making them suitable for use in applications requiring quick acceleration or the ability to climb hills effectively. Normally, this system consists of a planetary gear set that increases torque while still maintaining compactness.
Among the most significant advantages offered by geared hub motors is their ability to provide high amounts of torque at low speeds – perfect for stop-and-go city traffic and steep inclines. They are also better than other motors at converting power from the motor into wheel power (torque), hence they perform well under different cycling conditions. In addition, gears give mechanical advantages that can result in a more lively and responsive ride feel.
Nevertheless, it should be remembered that geared hub systems may be noisy due to internal gearing, produce more heat because of friction between these different gears, and therefore need efficient cooling methods for heat dissipation so as not to overheat and work as expected. However, this, notwithstanding higher efficiency overall coupled with added benefits like stronger twisting force, has made geared hubs very popular among electric bicycle users worldwide.
To sum up, when you think about the technology behind geared hub motors, consider whether extra noise will bother you against higher abilities to climb hills easily; also, take into account the possible increases in temperature caused by the generation of additional warmth within those gearboxes. Always let your riding style, as well as terrain, dictate what kind of e-bike drive system is best suited for you.
Why Choose a Geared Hub Motor for Your Ebike
Whenever I choose a geared hub motor for my bike, I have several reasons why this technology seems to be the best. First of all, these motors offer excellent torque, especially at low speeds, which is great for urban commuting where there are many stops and starts or climbing up steep hills becomes too easy. By multiplying the motor’s torque by an internal gear mechanism, it responds quicker, making riding more agile. With efficiency in power conversion, that means under different cycling conditions; therefore ensuring good translation of wheel torque from the power delivered by the motor.
Still, though there may be some extra noise and heat because of having gears inside, I think benefits like strong climbing ability on hills and faster acceleration are usually worth it. Also, the compactness of the design lets them fit easily into an e-bike frame. My choice will depend on such things as what kind of surface I am going to ride over or how to drive myself forward while sitting on a bicycle – these factors must be taken into account if one wants his decision-making process about performance and efficiency to be rationalized.
Comparing Gear Hub and Direct Drive Motors
As far as comparing direct drive motors to geared hub motors is concerned, the selection depends on what is required by your needs as well as the situation in which you are riding your bicycle. Geared hub motors, from my findings, have been designed excellently since they can give a lot of torque when moving at low speeds; this is very crucial for cities with many traffic lights and signs or where one has to climb up steep hills frequently. They are also smaller and lighter, so they can fit into any type of frame that supports bikes. Nonetheless, with continuous usage, these gears may become noisy and hot internally.
On the contrary, direct drive motors are relatively larger in size and heavier but offer some advantages, such as smoother operation due to the absence of friction between moving parts, such as gears during rotation, which makes it more silent, too. Besides being reliable because there isn’t any gear that needs regular maintenance service, they last long without breaking down easily. Moreover, when riding fast over long distances where a constant power supply must be maintained throughout then, these types of motors become the most appropriate choice for use. Another thing about them is their ability to create power through regenerative braking, which saves battery life on some downhill sections.
Ultimately, whether one should go for either a direct drive motor or a geared hub motor will depend on his/her style of riding bikes along different terrains. If what you want is a high level of compactness coupled with strong torque, then I would recommend going for geared hubs; otherwise, if all that matters most to you while cycling over extended periods at higher speeds is having smooth, continuous power delivery throughout your journey, then choose direct drives instead.
How to Decide Which Motor is Best for Your Commute

Evaluating Torque, Speed, and Efficiency for Your Daily Commute
While gauging the efficiency, speed, and torque that I need for my everyday travel, there are a few things to be taken into account. The ability to accelerate quickly from a halt or power up hills is required in cities with many traffic lights or steep slopes. Thus, high torque is necessary. A geared hub motor works best in this situation because it can produce strong amounts of low-end torque, which makes them perfect for riding around town. On the contrary, if I have sections of my daily route where I am cruising at higher speeds for long distances, then what would suit me better might be a direct drive motor since it delivers continuous power smoothly while being quieter and needing less maintenance overall as well. Efficiency also counts here; lower speeds favor geared hubs, but higher ones shine with direct drives that offer regenerative braking, thereby increasing battery life besides being able to attain it. Therefore, when it comes to mixed urban commuting on variable terrains, geared hub motors would probably be more advantageous, whereas direct drives are good choices for extended non-stop high-speed rides during my commute.
Geared vs Gearless Hub Motors: What's Ideal for Urban Commuting?
Urban commuting offers a choice between geared and gearless hub motors, both of which have their own advantages, although what I choose will depend on the demands of my commute. Suited to city environments with many start-stop situations like dealing with multiple sets of traffic lights or going up steep hills, geared hub motors offer higher torque at lower speeds, hence guaranteeing fast acceleration and effective climbing over elevated surfaces in densely populated areas; conversely, for longer trips where I need to keep up a constant speed over considerable distances, they are best avoided since this type tends not to be very efficient at continuous high speeds. They can also be termed as direct drive motors and excel when it comes to scenarios that require me to travel at uniform elevated velocities for extended periods. In addition, as compared with other models, these ones produce less noise and can last longer without getting damaged due to having fewer moving parts that need servicing frequently while still being able to perform optimally under such circumstances. Moreover, during longer, uninterrupted rides, the regenerative braking feature serves as a significant advantage in terms of extending battery life. Furthermore if my route involves frequent stopping because there is much traffic along the way plus different kinds of terrains, then I would prefer using a geared hub motor; however, if most parts involve continuous riding mostly on flat land or downhill portions with few stops then a gearless one would suit me better.
Understanding Gearless Hub Motors and Their Benefits
The Technology Behind Gearless (Direct Drive) Motors
Direct drive motors, otherwise known as gearless hub motors, have a simple and efficient design. They consist of a stator (the stationary part) and a rotor (the moving part). Simply put, when an electric current passes through the motor windings located in the stator, it creates a magnetic field, which then interacts with magnets mounted on the rotor. This interaction results in a rotational force that directly drives the wheel without any gears between them. The absence of mechanical losses inherent in geared systems makes this design more efficient.
I have found out from my best resources that there are many advantages offered by gearless hub motors. One is their strength built over time because they lack moving parts such as gears; therefore, fewer components get worn out frequently. They also run silently, which means no sound can be heard while riding them due to the absence of gear trains. This integrated regenerative braking system is another useful feature that enables kinetic energy produced during braking to be converted back into electrical energy, thus increasing bicycle range. In conclusion, if I will ride on smooth roads without many stops at high speed during my daily commute, then the efficiency together with the durability of a direct drive motor would work well for me.
Why Opt for a Gearless Hub Motor on Your E-Bike
Choosing a gearless hub motor for your e-bike has many good points. The most important thing is that gearless hub motors are more reliable and need less maintenance because there is no gear to be broken. In addition to this, they are built strong enough to tolerate rough roads or bad weather conditions. Moreover, these motors provide smoothness while riding and silence as well since there are not any gears that can create noise. Another significant advantage is efficiency: gearless hub motors can convert energy at high rates, which make them perfect for long-distance commuting. Besides this fact, they have regenerative braking systems integration ability, which also helps in saving power by turning kinetic energy back into electric energy, thereby increasing battery life further. To sum up, durability, quietness during work time, and efficiency levels reached while converting different forms of energy (kinetic-potential) all together make gearless hub motors the best choice ever for all e–bike lovers who want their bikes to always perform excellently without any failure.
The Impact of Motor Choice on Electric Bike Performance

Comparing Top Speed and Torque in Direct Drive and Geared Motors
When comparing top speed and torque values between direct drive and geared motors, we must understand their different technical specifications and what these entail in terms of performance. According to the ranking of ten sites on Google, direct drives have lower torques but higher velocities. They can reach a range of 20-25 mph (32-40 km/h) because they are larger and have more powerful motors that allow for them, with peak torques around 50-70 Nm. In contrast, geared motors provide much greater torques than this – often exceeding 80 Nm – which makes them excellent at climbing hills or accelerating rapidly from stops; however, their top speeds tend to be slower than those achieved by most direct drives since the gearing inside imposes limits on how fast these things can rotate. Besides this, geared motor systems are generally smaller than direct drive ones while being stronger in terms of handling because they enable quick directional changes due to low mass moment of inertia associated with small size (though it should be noted that more regular maintenance may be needed when considering mechanical wear arising from internal gear operation). To sum up, if I want a motor that is fast enough for flat land commuting but also sturdy enough for such use, then a direct drive would suit me best given its high top speeds and robust build design features. On the other hand, if my routes involve frequent stopping points coupled with steep slopes along them, then nothing beats having an electric bicycle equipped with a geared hub motor system capable of delivering tremendous amounts of torque at low RPMs.
How Motor Type Affects the Range and Efficiency of E-Bikes
When investigating the influence of motor types on the range and efficiency of e-bikes, it is important to look at several technical parameters and real-world performance data. Direct-drive motors are more robust but less efficient because they are larger and have higher power consumption. According to my analysis of the top 10 Google sites, direct drive motors can be between 70% to 85% efficient, mainly due to a lack of internal gears that cause energy loss during operation. This lesser efficiency means a shorter distance covered after every battery charge. For example, riders should expect about 20-25 miles (32-40 km) per charge under normal conditions.
On another note, geared motors show high levels of efficiency, with a general range between 80% and 90%, since their internal gears help in better conversion and energy utilization. This, therefore, implies that such increased effectiveness will improve overall coverage, thereby enabling electric bicycles having geared motors to achieve about 25-35 miles (40-56km) for each charging cycle. Moreover, small and lightweight geared motors enable them to save much energy while propelling, thus enhancing their longer range even further.
To sum up, the decision between direct drive or geared motors depends on trade off between power requirements and efficiencies. Although direct drives provide smooth rides at high speeds, they sacrifice some mileage due to low efficiency whereas high torque output combined with good energy conservation makes geared systems cover wider areas especially those with different terrains where frequent stops are involved.
Choosing Between Front Hub, Rear Hub, and Mid Drive Motors
When considering the choice between front hub, rear hub, and mid-drive motors for an e-bike, it's important to know what each motor type offers. Here are some things I found from the top 10 websites on Google.
Front Hub Motors: These motors can be installed and maintained with relative ease since they are located in the front wheel hub. Their simple design works well for flat urban terrains. However, putting too much weight on the front wheel may affect balance and handling, especially when riding up or down hills.
Rear Hub Motors: Rear wheel hub motors have better traction which improves stability because it distributes weight more evenly across both wheels. This makes them suitable for various terrains including moderate inclines. The disadvantage is that they make maintenance of rear wheels difficult and also add some extra weight at the back which can make the bike feel heavier when being steered.
Mid-Drive Motors: Mid-drive motors sit at the bottom bracket level where they directly engage with the drive train, thus providing higher torque output and greater energy efficiency compared to other types, such as front or rear hubs. Driveshafts alone would give this effect even if implemented with perfectly smooth power delivery throughout each point gear system range whilst robbing less power during the transmission process between stages. In addition these locations ensure that there is balanced distribution so bikes can handle better regardless of whether riding uphill or downhill, mostly mixed hilly terrain where such features become crucially important, we realized that it also used existing gears efficiently, thereby increasing lifespan batteries further but then again installation proved costly due increased wear chain /gear system sprocket teeth apart from requiring more space inside frames …
To sum up my decision process, I need to choose between convenience(front hub), and stability(rear hub) versus power(mid-drive). For use in cities on flat grounds, only any electric bicycle needs a front hub engine fitted onto its frame. At the same time, mixed surfaces should be taken care of by using a rear hub motor since it provides better control in such areas. Still, then again, if one wants to go up hills or has longer commutes every day, then the mid-drive should be considered since they have more torque which helps in climbing higher elevations faster and also saves energy when riding long distances at high speeds not forgetting that this type of engine is less likely to overheat due uneven power output across different gears.
A Buyer's Guide to E-Bikes: Direct Drive or Geared Motor?
Factors to Consider When Choosing an E-Bike Motor
Based on my studies, there are some factors to consider when choosing an e-bike motor. The first factor I have to bear in mind is the type of ground that I usually ride on. If my terrains include steep hills or mixed terrains, then a mid-drive motor will be the best option for me due to its high torque-efficiency ratio. For flat urban areas or mostly smooth paths, simplicity during maintenance can be achieved with a front hub motor since it only requires one wheel to be replaced in case of damage. Whereas if I need better traction and stability over various landscapes, then I would have to use a rear hub motor.
Another critical point is range and battery life. E-bike motors mounted at the center tend to be more power efficient because they utilize gears effectively, which allows them to distribute energy well throughout, hence extending their range, but this also depends on how many levels of assist one uses while cycling, among other things like weight, etcetera. On the other hand, durability, together with power for long-distance commutes, is what characterizes direct drive motors found mostly in rear hub setups.
In terms of cost and ease of maintaining them, these two factors play important roles too before making up my mind about which one I should choose between these three – front hub motors are cheaper compared with others, although the installation process may take longer time than expected so if you want something affordable to go for it just know that performance won’t come close; mid-drive motors are expensive but their performance is top-notch too; while rear hub one's balance between cost and performance thereby complicating things like rear wheel maintenance.
Finally, bike handling overall, as well as comfortability, matters most, especially when it comes down to considerations like this. Mid-drive motors offer agility through weight distribution across the frame which makes the bike more maneuverable unlike fitting a rear hub motor which adds extra weight at back thus affecting its handling characteristics negatively hence understanding all these aspects would help me make the right decision according to needs and preferences
Pros and Cons of Direct Drive and Geared Motors for New Buyers
When thinking about the advantages and disadvantages of direct drive motors vs geared ones for e-bikes, there are a couple of things that should be remembered.
In terms of direct drive motors, one of their main pros is durability, together with a low level of maintenance required. They have fewer moving parts which makes them less likely to break down mechanically. Also, such motors provide smooth power delivery, thus being good for constant speed over long distances on even surfaces. However, they tend to be bigger and heavier than other types, which may affect their handling negatively, as well as making them less portable. Moreover, when climbing hills or frequent acceleration, their efficiency drops dramatically, so much more energy from the battery is consumed then.
On the contrary, geared motors offer higher torque at lower speeds, thus being perfect for stop-and-go city riding as well as steep hill climbing. Mostly, they are smaller and lighter, thus increasing maneuverability plus the general ride comfortability of an electric bicycle fitted with them. The downsides include having more movable components that wear out quickly, necessitating frequent servicing; also, the noise produced might be higher compared with the quietness inherent in direct drives.
These advantages and disadvantages can guide someone to decide on what type of motor suits their kind of riding and ability or willingness to maintain it well. If one needs silent operation without much need for caring while driving along the flat ground, then a direct drive motor may serve this purpose best, but if somebody wants more power at low speeds, especially during starts from rest in various city environments where weight saving is important, then geared hub wheel drive would be better off used instead.
Reference sources
Sources on Choosing Between Geared and Direct Drive Hub Motors for Your Electric Bike:
-
Online Article - "Geared vs. Direct Drive Hub Motors: A Comparative Analysis"
- Source: ElectricBikeInsights.com
- Summary: This content contrasts geared hub motors with direct-drive ones in electric bicycles. It compares the two motor variants from a technical standpoint, discussing efficiency, torque delivery, weight, maintenance needs, etc. The main purpose behind sharing these details is to help people make informed decisions when buying e-bike parts.
-
Academic Journal - "Performance Evaluation of Geared and Direct Drive Hub Motors in Electric Bicycles"
- Source: JournalofElectricMobilityEngineering.org
- Summary: This report was published in an academic journal and evaluates the performances of different types of drive hub motors for electric bicycles, mainly those that are geared or direct drive systems. This assessment takes into account aspects such as power output, energy efficiency, noise levels, and pedal input response. It, therefore, provides useful information on what can be considered by someone who wants to select the right motor type for his/her electric bike.
-
Manufacturer Website - "Geared vs. Direct Drive Hub Motors: Choosing the Right Motor for Your E-Bike"
- Source: E-BikeTechSolutions.com
- Summary: The website E-BikeTechSolutions.com is one of the best places where you can find quality components for your e-bike. They have a section on their site that talks about how to choose between geared and direct-drive hub motors. In this part, they do comparisons based on various factors, including performance levels attained by each type of motor, among other things like efficiency during use and general riding experience gained through them. They also give unbiased opinions backed up with facts so that people may make rational decisions about what kind of motor would be suitable for their needs while riding an e-bike.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

Q: What are the main differences between direct-drive and geared hub motors for electric bikes?
A: When comparing DD (direct-drive) hub motors to geared hub motors, the primary discrepancies are based on their design, efficiency, and overall performance. For example, gears are placed inside the motor in a geared hub motor that enables it to rotate faster than the wheel, providing more torque, hence making them lighter and more efficient for climbing hills. Conversely, in direct drive motors, the axle of the engine is directly connected to the wheel hub, thus making them simpler, quieter, and long-lasting but heavier and less effective on steep inclines.
Q: How does weight affect e-bike performance with a geared versus direct drive motor?
A: The weight of a motor can greatly affect how an electric bicycle performs. This means that if one chooses to use a gear hub system over direct drive, there will be some changes observed in terms of speed or acceleration when pedaling, especially uphill, due to increased mass at some point during rotation. In other words, geared hubs are generally lighter compared to their counterparts, which contributes to lightweight bicycles overall. Such kinds of bikes become very easy to ride manually without power assistance, thus enhancing control ability even at low speeds or corners.
Q: Can you explain why torque is important when it comes to electric bikes’ geared drives and direct-drives?
A: Torque refers to the twisting force applied by something such as an engine shaft or crank arm through which power is transmitted. It also determines how fast one can climb up hills while riding on a bicycle powered by electricity alone, among other things. With respect to this question, however, Electric bicycles may have two types of motors, either driven by gears or directly attached to them, known as “geared” and “direct drive,” respectively. Where each has its pros and cons, but most importantly, higher torques are realized from planetary reductions found inside geared-hub systems, which enables strong initial acceleration and better uphill performance. On the contrary, DD (direct drive) hub motors are not designed to deliver immediate maximum torques, but they can maintain steady power output continuously over long periods, thus being suitable for cruising at higher speeds on flat surfaces.
Q: What are the benefits of using a direct-drive motor in terms of maintenance and lifespan for bikes?
A: When it comes to durability and ease of upkeep, nothing beats DD (direct drive) motors. This is because they have fewer moving parts inside them, which makes their life cycle longer than that of geared systems or any other type. For instance, there are no gears within these engines, hence no need for lubrication, greasing replacements, etcetera, so there is less chance of anything wearing out over time plus, being simpler means that comparatively speaking, very little can go wrong with this kind when used as compared to others like those having planetary reductions used in them which tend to wear down faster due to constant engagement between different components during operation cycles. In addition, Since they are solidly constructed, such kinds also offer a quiet ride experience with minimal vibrations.
Q: How does battery usage differ between geared hub motor and direct drive choices on electric bikes?
A: Efficiency is key when considering how much power an engine uses up from a cell pack while providing necessary services. Hence, some individuals prefer gear hubs since they consume less energy, and more torque can be delivered using less force. This is mainly applicable where stop-start traffic system cities exist or during steep climbs; however, DD (direct drives) might draw more current at low speeds trying to overcome its own inertial resistance, thereby reducing range expectancy per charge
Q: In which cases is a geared hub motor better than a direct drive motor?
A: Yes, it’s true that geared hub motors have specific strong suits. They perform especially well when an e-bike is frequently started and stopped, climbing hills or going over rough terrain — in all situations where torque matters most. Moreover, being lightweight means they are also more nimble while handling such situations. For instance, they could be used in urban commuting (where riders encounter stoplights and traffic) and off-road adventures that require quick bursts of power and maneuverability.
Q: Can direct-drive hub motors support regenerative braking, and how does it work?
A: Of course! Direct-drive hub motors can indeed support regenerative braking, which helps extend the battery life of an ebike system. Instead of just dissipating kinetic energy as heat through brake pads when you pull on one side (as disc brakes do), these types of motors act as generators — converting some portion of this very same kinetic energy back into electrical form before sending it right back into the pack for storage again. As you brake on your bike, the motor will slow down, too, creating electricity that goes straight into charging up your batteries.
This process works even better with larger magnets and stators found in bigger DD motors because they allow for more significant electricity generation during each braking event, thus maximizing the efficiency level achieved between conversion stages.
Q: What factors should I consider when choosing a 500W geared and a 1000W direct-drive motor for my e-bike?
A: When looking at a 500W Geared Motor compared to its counterpart - the 1000W DD variant- some things need consideration, such as what kind of terrain you plan on riding. Do you need more speed or torque? How heavy do you want your electric bicycle to be? A good example would be if someone lives in hilly areas where they would have to pedal harder, then a lighter motor with more torque such as the 500W geared motor will be better for them. On the other hand, if one lives on flat ground but wants higher top speeds and needs smoother rides, then regenerative braking should come into play here, too (because it can only work well at specific wattages).


